Center for Immigration Studies
CIS.org
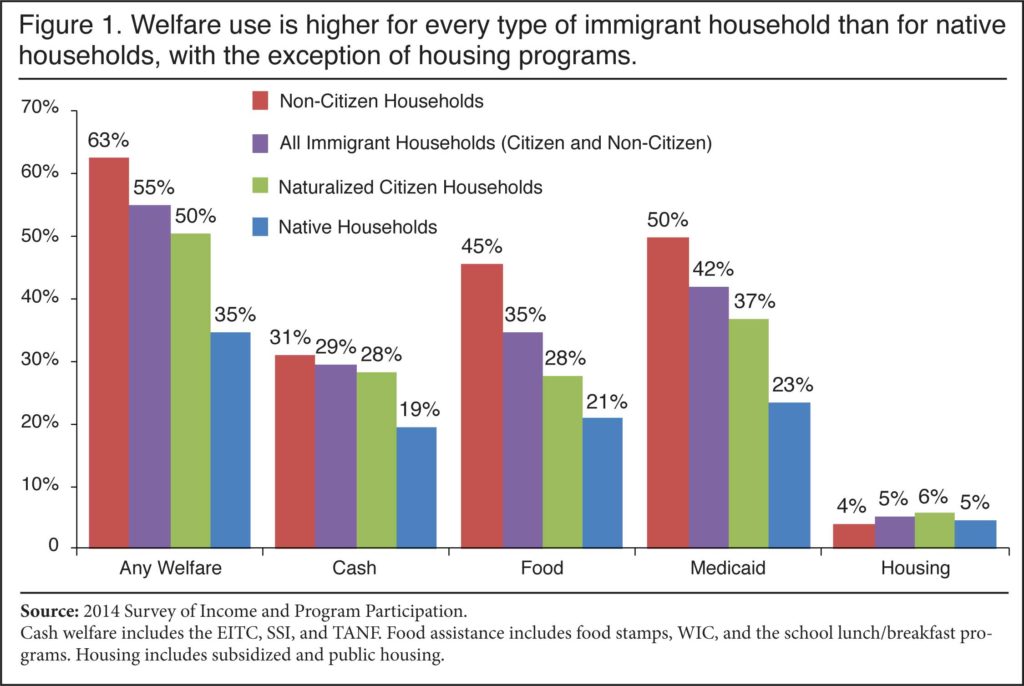
63% of Non-Citizen Households Access Welfare Programs
Compared to 35% of native households
Download a PDF of this Backgrounder.
Steven A. Camarota is the director of research and Karen Zeigler is a demographer at the Center.
New “public charge” rules issued by the Trump administration expand the list of programs that are considered welfare, receipt of which may prevent a prospective immigrant from receiving lawful permanent residence (a green card). Analysis by the Center for Immigration Studies of the Census Bureau’s Survey of Income and Program Participation (SIPP) shows welfare use by households headed by non-citizens is very high. The desire to reduce these rates among future immigrants is the primary justification for the rule change. Immigrant advocacy groups are right to worry that the high welfare use of non-citizens may impact the ability of some to receive green cards, though the actual impacts of the rules are unclear because they do not include all the benefits non-citizens receive on behalf of their children and many welfare programs are not included in the new rules. As welfare participation varies dramatically by education level, significantly reducing future welfare use rates would require public charge rules that take into consideration education levels and resulting income and likely welfare use.
Of non-citizens in Census Bureau data, roughly half are in the country illegally. Non-citizens also include long-term temporary visitors (e.g. guestworkers and foreign students) and permanent residents who have not naturalized (green card holders). Despite the fact that there are barriers designed to prevent welfare use for all of these non-citizen populations, the data shows that, overall, non-citizen households access the welfare system at high rates, often receiving benefits on behalf of U.S.-born children.
Among the findings:
- In 2014, 63 percent of households headed by a non-citizen reported that they used at least one welfare program, compared to 35 percent of native-headed households.
- Welfare use drops to 58 percent for non-citizen households and 30 percent for native households if cash payments from the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) are not counted as welfare. EITC recipients pay no federal income tax. Like other welfare, the EITC is a means-tested, anti-poverty program, but unlike other programs one has to work to receive it.
- Compared to native households, non-citizen households have much higher use of food programs (45 percent vs. 21 percent for natives) and Medicaid (50 percent vs. 23 percent for natives).
- Including the EITC, 31 percent of non-citizen-headed households receive cash welfare, compared to 19 percent of native households. If the EITC is not included, then cash receipt by non-citizen households is slightly lower than natives (6 percent vs. 8 percent).
- While most new legal immigrants (green card holders) are barred from most welfare programs, as are illegal immigrants and temporary visitors, these provisions have only a modest impact on non-citizen household use rates because: 1) most legal immigrants have been in the country long enough to qualify; 2) the bar does not apply to all programs, nor does it always apply to non-citizen children; 3) some states provide welfare to new immigrants on their own; and, most importantly, 4) non-citizens (including illegal immigrants) can receive benefits on behalf of their U.S.-born children who are awarded U.S. citizenship and full welfare eligibility at birth. Read the entire report here.